Slow Log Queries Optimization Service is a specific type of service specifically designed to make databases more efficient. It functions on the concept of SQL queries that lead to slower systems. It optimizes slow queries and, in the process, improves general database efficiency so applications and services are delivered promptly and reliably to users. Here's a clear depiction of how this service functions, along with its features and benefits:
Key Components and Processes
1. Slow Query Detection:
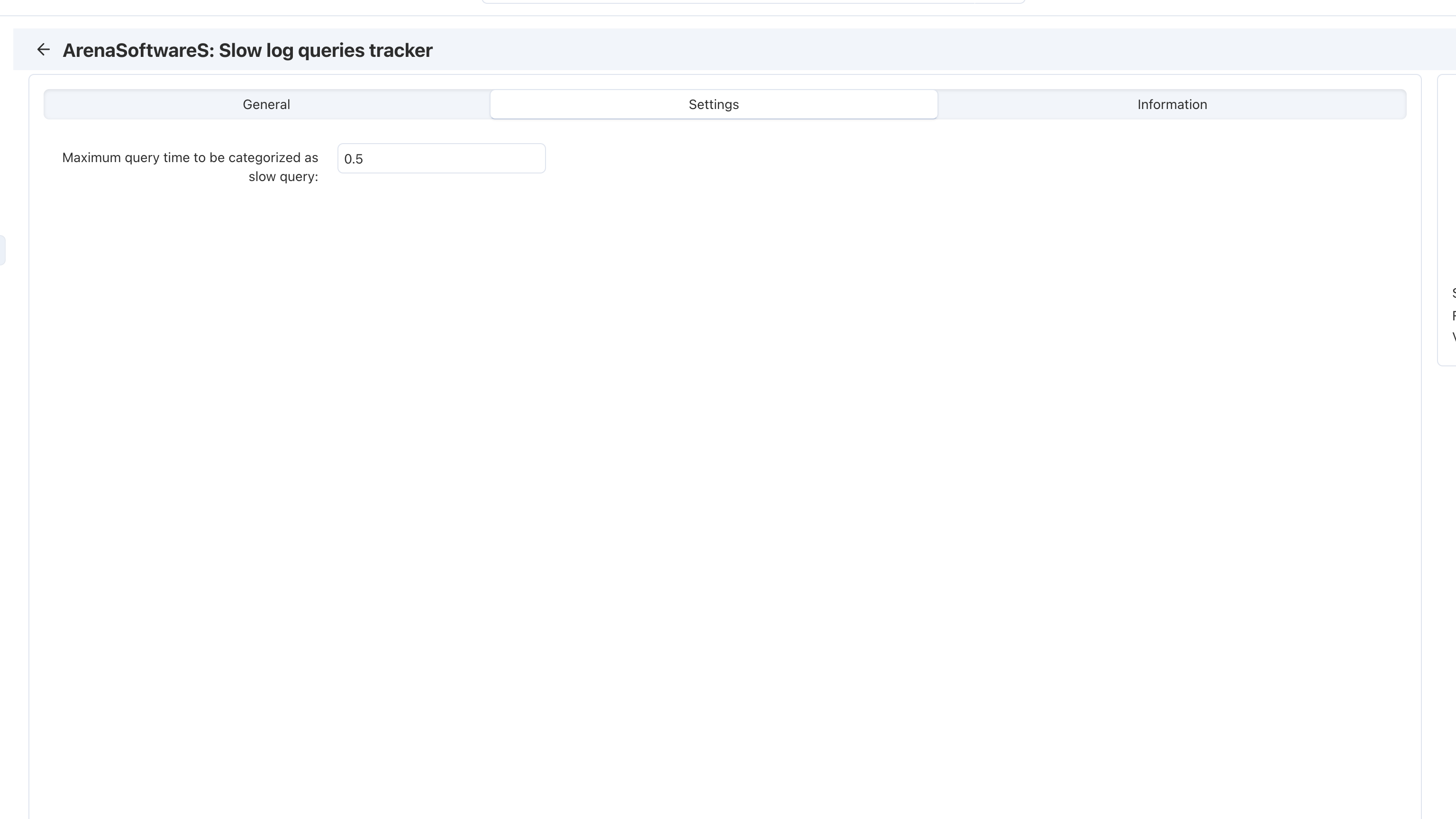
- It can continue to monitor the database and pinpoint queries for which run times exceed the accepted time, usually through slow query logs created by the database. Most database systems, including MySQL and PostgreSQL, will automatically create slow query logs that record queries taking longer than a threshold.
- Monitoring these logs would identify problematic queries for a service so that database administrators can make the greatest impact by optimizing SQL operations performance.
2. Query Profiling:
- Query profiling details are used to dig further into the specifics of slow-running queries to understand why they are underperforming. This process breaks down each query to analyze factors causing slow performance - joins, subqueries, indexing, etc.
- Profiling may include analyzing the execution plans for queries- the sequence of operations that databases use to execute any query. From this, the service detects the bottlenecks in the queries, such as inefficient join operations, unnecessary sorting operations, or scanning large tables.
3. Recommendations for Query Optimization: The service provides specific recommendations that improve the performance of a slow query after profiling it. Recommendations might include:
- Indexing: An index on columns used to potentially offset lookup times when building query conditions.
- Changes in Query Structure: Queries can sometimes be simplified by reducing execution time or by breaking down into subqueries.
- Changes in Database Configuration: Memory cache can sometimes improve performance on certain operations against a database.
This best practice allows DBAs to make directed, workload-specific changes to every database.
4. Auto-Query Tuning:
- For more performance-critical databases, manual tuning becomes time-consuming. Automatic tuning addressed the issue by applying some optimization techniques like indexing or query rewriting directly to identified slow queries.
- The automated process will help minimize time to resolve performance problems and place the databases back to their responsive state without constant manual intervention.
5. Performance Monitoring:
- Even after the optimization, the service continues to track the database behavior as far as performance is concerned. This step ensures effectiveness in the long term and that new issues can be easily spotted.
- Monitoring helps ensure that optimization efforts have been fruitful through consistent improvements while monitoring the general health of the database.
6. Analysis of Resource Usage:
- Apart from their execution time, queries can also tend to consume a lot of CPU, memory, or I/O resources when concerned about particular calculations or dealing with extremely large datasets.
- It offers an analysis of the resource consumption for every query to identify exact resource-consuming queries. The administrators may then carry out focused optimizations to minimize the load on the system.
7. Customizable Alerts
- Alerts can be configured to notify the administrators if a query is taking too long to return within any predefined time duration so that slow queries are taken care of right away.
- This may add another dimension of responsiveness, especially in heavily trafficked applications or real-time applications that take a serious hit in case of performance issues.
8. High-Level Reporting:
- It gives comprehensive reports of how queries are trending over time and marks where optimizations have indeed worked and which ones need further improvement.
- These reports help database administrators and stakeholders to analyze efforts made in the direction of optimizations for subsequent performance-tuning activities.
Benefits of Slow Log Queries Optimization Service
- Improved Performance: This database directly slows down the queries so that the application will run smoothly, thus implying a better performance to end users.
- Operational Efficiency: With the capability of automated database tuning and optimization, there are decreased manual interventions, hence allowing database administrators to focus on other crucial issues.
- Scalability: Service query optimization allows databases to take increased workloads without the proportionate increase in hardware resources.
- Cost Savings: Optimization in performance means a lesser load on the resources of the CPU and memory, possibly saving organizations money in infrastructure by a reduction in the need for additional hardware or cloud resource scaling.
- Actionable Insights: Profiling, monitoring, and reporting provide deep database performance insights that can be used to help an organization make data-driven decisions to continually improve performance.
In short, the Slow Log Queries Optimization Service represents something of high value for any organization striving to develop quality, high-performance applications based on databases. Indeed, attention to identification, analysis, and continuous optimization of slow queries is what improves both speed and efficiency in databases, directly and indirectly benefiting users and administrators.
No data found
No reviews found